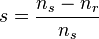An induction or asynchronous motor is an AC electric motor in which the electric current in the rotor needed to produce torque is obtained by electromagnetic induction from the magnetic field of the stator winding. An induction motor therefore does not require mechanical commutation, separate-excitation or self-excitation for all or part of the energy transferred from stator to rotor, as inuniversal, DC and large synchronous motors. An induction motor's rotor can be either wound type or squirrel-cage type.
Three-phase squirrel-cage induction motors are widely used in industrial drives because they are rugged, reliable and economical. Single-phase induction motors are used extensively for smaller loads, such as household appliances like fans. Although traditionally used in fixed-speed service, induction motors are increasingly being used with variable-frequency drives (VFDs) in variable-speed service. VFDs offer especially important energy savings opportunities for existing and prospective induction motors in variable-torque centrifugal fan, pump and compressor load applications. Squirrel cage induction motors are very widely used in both fixed-speed and VFD applications.
Synchronous speed
An AC motor's synchronous speed,  , is the rotation rate of the stator's magnetic field, which is expressed in revolutions per minute as
, is the rotation rate of the stator's magnetic field, which is expressed in revolutions per minute as
 , is the rotation rate of the stator's magnetic field, which is expressed in revolutions per minute as
, is the rotation rate of the stator's magnetic field, which is expressed in revolutions per minute as (RPM),
(RPM),
slip
Slip,  , is defined as the difference between synchronous speed and operating speed, at the same frequency, expressed in rpm or in percent or ratio of synchronous speed. Thus
, is defined as the difference between synchronous speed and operating speed, at the same frequency, expressed in rpm or in percent or ratio of synchronous speed. Thus
 , is defined as the difference between synchronous speed and operating speed, at the same frequency, expressed in rpm or in percent or ratio of synchronous speed. Thus
, is defined as the difference between synchronous speed and operating speed, at the same frequency, expressed in rpm or in percent or ratio of synchronous speed. Thus
where  is stator electrical speed,
is stator electrical speed, 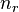 is rotor mechanical speed.[9][28] Slip, which varies from zero at synchronous speed and 1 when the rotor is at rest, determines the motor's torque. Since the short-circuited rotor windings have small resistance, a small slip induces a large current in the rotor and produces large torque.[29] At full rated load, slip varies from more than 5% for small or special purpose motors to less than 1% for large motors.[30] These speed variations can cause load-sharing problems when differently sized motors are mechanically connected.[30] Various methods are available to reduce slip, VFDs often offering the best solution.[30]
is rotor mechanical speed.[9][28] Slip, which varies from zero at synchronous speed and 1 when the rotor is at rest, determines the motor's torque. Since the short-circuited rotor windings have small resistance, a small slip induces a large current in the rotor and produces large torque.[29] At full rated load, slip varies from more than 5% for small or special purpose motors to less than 1% for large motors.[30] These speed variations can cause load-sharing problems when differently sized motors are mechanically connected.[30] Various methods are available to reduce slip, VFDs often offering the best solution.[30]
 is stator electrical speed,
is stator electrical speed, 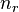 is rotor mechanical speed.[9][28] Slip, which varies from zero at synchronous speed and 1 when the rotor is at rest, determines the motor's torque. Since the short-circuited rotor windings have small resistance, a small slip induces a large current in the rotor and produces large torque.[29] At full rated load, slip varies from more than 5% for small or special purpose motors to less than 1% for large motors.[30] These speed variations can cause load-sharing problems when differently sized motors are mechanically connected.[30] Various methods are available to reduce slip, VFDs often offering the best solution.[30]
is rotor mechanical speed.[9][28] Slip, which varies from zero at synchronous speed and 1 when the rotor is at rest, determines the motor's torque. Since the short-circuited rotor windings have small resistance, a small slip induces a large current in the rotor and produces large torque.[29] At full rated load, slip varies from more than 5% for small or special purpose motors to less than 1% for large motors.[30] These speed variations can cause load-sharing problems when differently sized motors are mechanically connected.[30] Various methods are available to reduce slip, VFDs often offering the best solution.[30]
Types Induction Motor
- Split phase induction motor
- Capacitor start induction motor
- Capacitor start capacitor run induction motor
- Shaded pole induction motor
- Squirrel cage induction motor
- Slip ring induction motor
We had mentioned above that single phase induction motor is not a self starting and three phase induction motor is self starting. So what is self starting? When the machine starts running automatically without any external force to the machine, then it is called as self starting. For example we see that when we press the key the fan starts to rotate automatically, so it is self starting. Point to be note that fan used in home appliances is single phase induction motor but it is self starting. How? We will discuss it how.
Why is Three Phase Induction Motor Self Starting?
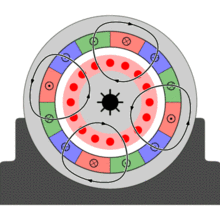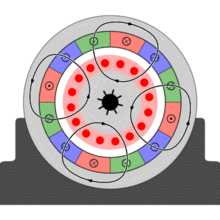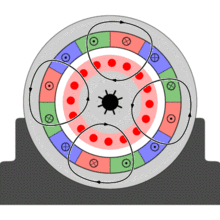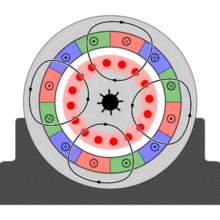
In three phase system, there are three single phase line with 120° phase difference. So the rotating magnetic field is having the same phase difference which will make the rotor to move. If we consider three phases a, b and c, when phase a is magnetized, the rotor will move towards the phase a winding, in the next moment phase b will get magnetized and it will attract the rotor and than phase c. So the rotor will continue to rotate.
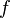 is the motor supply's frequency in hertz and
is the motor supply's frequency in hertz and 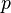 is the number of magnetic poles.
is the number of magnetic poles.